The Iron Age (c. 1200-600 BCE)
A decline of the people’s economic status can be seen through the finds belonging to the next major settlement at Tell Abu al-Kharaz belonging to the Iron Age, starting around 1200 BC. It was a period of wars caused mainly by the so-called “Sea-peoples” and the Philistines invading Palestine. More coarse pottery and no imported materials are typical for that period. The city wall from the Iron I period indicates a continuing need for defensive systems, and the architectural remains from the Iron II period includes towers and well built houses whose people again imported goods from the eastern Mediterranean region.
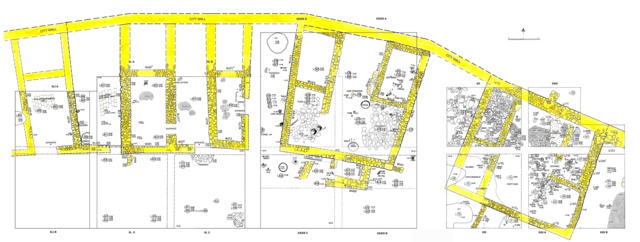
Four s.c. 4-room houses from Area 7 at Tell Abu al-Kharaz.
Among the finds from the Iron Age II period is an exquisite decorated bone handle with a motif of two sphinxes. Parallels with this object are from Hazor in northern Palestine and Nimrud in Assyria, however it is very likely the product of a Palestinian workshop (see below left).

Bone handle with a motif of two sphinxes.

A clay mask of a bearded and smiling young male painted in red.
Other interesting Iron Age II finds include a clay mask of a bearded and smiling young male painted in red, attached originally to an anthropomorphic vessel (see above right) and a complete clay rhyton of a donkey with two attached miniature vessels (see below).

Clay rhyton of a donkey.
A decorated cosmetic plate of polished limestone should be mentioned (see below; observe the remains of a blue substance, possible powder of lapis lazilu, in the depressions).

A decorated cosmetic plate of polished limestone.
